Gout is a common cause of inflammatory arthritis cause by crystals forming in the joint. This results in recurring attacks of intense swelling, heat and redness of an affected joint. Flares of gout usually come on suddenly and within 24 hours can build into a very severe pain. A typical attack of gout will usually settle over 7 to 10 days, and in between attacks symptoms usually resolve completely.
Gout can affect any joint in the body, and can affect many joints at the same time, however most commonly it will affect a single joint at a time, usually the base of the big toe.
Gout is more common in men than in women, and it becomes more common with increasing age. Gout currently affects about 1 in 40 of the general population in the United Kingdom, however in men over the age of 70 this increases to about 1 in 10 of the population.
Gout is caused by crystals of urate that form in the joints. The crystals can rub against the joint lining (synovium) causing inflammation.
Urate is a normal break down product of purines. Purines are present in our cells and certain foods. Urate circulates in the blood and is usually passed harmlessly in the urine. However if the kidneys cannot get rid of the excess, or the body produces too much, levels in the body become raised (hyperuricaemia) and crystals can form within the joints, or under the skin.
High uric acid levels can be caused by kidney problems, drug treatments (particularly water tablets for high blood pressure or heart failure), as well increasing body weight and diet.

Gout flare
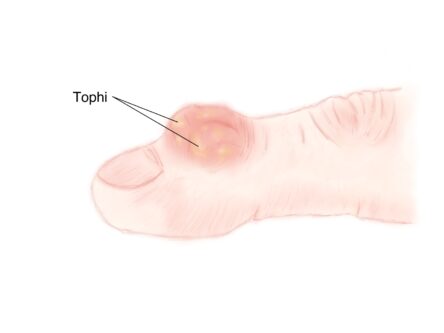
Tophi
Diagnosis is made based on the history of presentation and examination. The typical presentation of recurrent attacks of pain, redness and swelling in the big toe of a middle aged man is classical.
Joint aspiration:
Blood urate levels:
There are two key parts to the treatment of gout. Immediate and longer term treatment.
Immediate treatments:
Longer-term treatments:
In newly diagnosed individuals, or patients with severe tophaceous disease the target blood urate level is 0.3mmol/l or lower. Therefore medications can be gradually increased to reach this target. In severe tophi, it can take months to years to clear the crystal build up.
Versus Arthritis: http://www.versusarthritis.org
UK Gout society: http://www.ukgoutsociety.org